Working with the Conref Push Mechanism
Content Reference Push Mechanism
The usual method of using content references pulls element content from a source element and inserts it in the current topic. DITA 1.2 introduced an alternative method of content referencing, allowing element content to be pushed, or injected, from a source topic to another topic without any special coding in the topic where the content will be re-used. This technique is known as a content reference push mechanism (conref push).
The conref push mechanism requires elements in the target topic (the topic where the content is to be pushed) to have ID elements, as the push mechanism inserts elements before or after a named element, or replaces the named element. Assuming the source topic is included in the DITA map, the conref push will be processed during the publishing stage for the DITA map.
Example of a Conref Push Scenario
An example of a scenario where a conref push would be useful is where a car manufacturer produces driver manuals that are distributed to various regions with their own specific regulations and certain sections need to be customized by the local car dealers before publishing. The local dealer could use a conref push technique to insert specific content without modifying the manufacturer-supplied content.
Push Current Element Action
Oxygen XML Editor Eclipse plugin includes an action that allows you to easily reference content with a conref push mechanism. The Push Current Element action is available in the DITA menu and in the Reuse subfolder of the contextual menu when editing in Author mode. Selecting this action opens the Push current element dialog box that allows you to select a target resource and element, and where to insert the current element content.
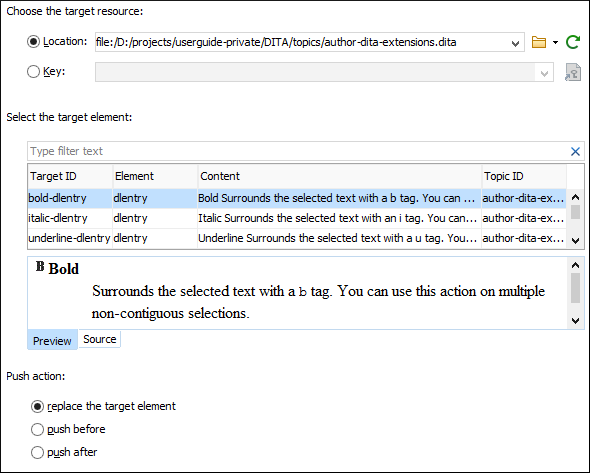
- Choose the target resource
- Allows you to select a Location URL or a Key for the target resource and the table in the next section of the dialog box will be populated using the information from the specified resource.
- Select the target element
- The table in this section contains the available elements (identified by their ID) that can be replaced by, or pushed before/after, the current element, according to the push action.
- Push action
-
Allows you to choose one of the following options for where you want to insert the current element content:
- replace the target element
-
The target element will be replaced with the current element content.
On the technical side, the value of the
@conactionattribute in the current element will be set topush replaceand the@conrefor@conkeyrefattribute will be set to the specified reference. - push before
-
The current element content will be inserted before the specified target element in the target resource.
On the technical side, the value of the
@conactionattribute in the current element will be set topushbefore. Another element with the same name and class as the target element will be inserted in the document after the current element. The new element will have the@conactionattribute set tomarkand the@conrefor@conkeyrefattribute will be set to the specified reference. - push after
-
The current element content will be inserted after the specified target element in the target resource.
On the technical side, the value of the
@conactionattribute in the current element will be set topushafter. Another element with the same name and class as the target element will be inserted in the document before the current element. The new element will have the@conactionattribute set tomarkand the@conrefor@conkeyrefattribute will be set to the specified reference.
You can also use the Preview panel to view the content that will be pushed and the Source panel to see the XML code for the content to be pushed. After you click OK, the conref push mechanism is inserted in the current document. The changes in the target resource will be processed when you transform the DITA map.
Resources
For more information about the conref push mechanism and other advanced DITA profiling concepts, watch our Webinar: Working with DITA in Oxygen - Advanced Profiling and Reuse Strategies.
