XSD to JSON Schema Converter
Oxygen XML includes a tool for converting an XML Schema file (XSD) to a JSON Schema file. The XSD to JSON Schema action for invoking the tool can be found in the menu. It requires an additional add-on to be installed, so the first time you invoke the action, Oxygen XML will present a dialog box asking if you want to install it. Once installed, you need to restart Oxygen XML and the XSD to JSON Schema action will invoke the tool.
Quick Installation
You can drag the following Install button and drop it into the main editor in Oxygen to quickly initiate the installation process:
Manual Installation
- Go to to open an add-on selection dialog box.
- Enter or paste
https://www.oxygenxml.com/InstData/Addons/default/updateSite.xml in the
Show add-ons from field or select it from the drop-down
menu.Note:If you have issues connecting to the default update site, you can download the add-on package, unzip it, then use the Browse for local files action in the Install new add-ons dialog box to locate the downloaded addon.xml file.
- Select the XSD to JSON Schema add-on and click Next.
- Read the end-user license agreement. Then select the I accept all terms of the end-user license agreement option and click Finish.
- Restart the application.
Result: The XSD to JSON Schema dialog box is now available and can be selected from the menu.
Converting XSD to JSON Schema
To convert an XML Schema (XSD) to a JSON Schema, follow these steps:
-
Select the XSD to JSON Schema action from the menu.
Step Result: The XSD to JSON Schema dialog box is displayed:
Figure 1. XSD to JSON Schema Dialog Box 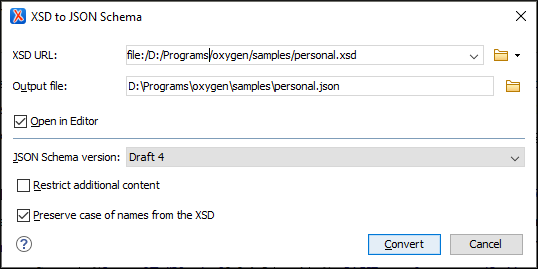
- In the XSD URL field, choose or enter the URL of the XML Schema document. The conversion supports XSD versions 1.0 and 1.1.
- In the Output file field, choose the path for the resulting output file.
- [Optional] You can select the Open in Editor option to open the resulting JSON Schema document in the main editing pane.
- For the JSON Schema version option, choose the version of the resulting JSON schema. The possible choices are: Draft 4, Draft 6, Draft 7, 2019-09, and 2020-12.
- [Optional] If you select the Restrict additional
content option, then
additionalProperties(for objects) andadditionalItems(for arrays) will be set tofalsein the resulting schema. By default, these keys are not in the schema, meaning that providing additional content (according to the schema) is allowed. - [Optional] You can select the Preserve case of names from
the XSD option if you want the names from the XSD to remain unchanged in the
resulting JSON Schema. Otherwise, the default JAXB naming algorithm will be applied (for
example, "
some.nAMe" is changed to "SomeNAMe", or "Some_oth3r_name" is changed to "SomeOth3RName"). - Click the Convert button.
- The
$idof the schema, generated from XSDtargetNamespace. - The
$definitionssection, which declarescomplexandenumtypes. - The
anyOfsection, which lists possible top-level elements as an array of objects.
- If an XSD type extends another type, then its schema is combined
with the schema of the base type using the
allOfkeyword. - If an extension in XSD defines an element with the same name as an
attribute in the base, a property named
restis generated to avoid name conflicts in JSON. - If a property of a complex type is a collection property, the schema of the collection items will be wrapped in the JSON array schema.
Conversion Mappings
The following table lists the specific conversion mapping details.
| XML Schema Type | JSON Schema Representation |
|---|---|
| anySimpleType | string, number, integer, boolean, null |
| anyType | string, number, integer, boolean, null, object, array |
| string | string |
| normalizedString | string |
| token | string |
| language | string |
| Name | string |
| NCName | string |
| ID | string |
| IDREF | string |
| IDREFS | array of strings |
| ENTITY | string |
| ENTITIES | array of strings |
| NMTOKEN | string |
| NMTOKENS | array of strings |
| boolean | boolean |
| base64Binary | array of integers |
| hexBinary | array of integers |
| float | number |
| decimal | number |
| integer | integer |
| nonPositiveInteger | integer |
| negativeInteger | integer |
| long | integer |
| int | integer |
| short | integer |
| byte | integer |
| nonNegativeInteger | integer |
| unsignedLong | integer |
| unsignedInt | integer |
| unsignedShort | integer |
| unsignedByte | integer |
| positiveInteger | integer |
| double | number |
| anyURI | string with "format":"uri" |
| QName | object with "namespaceURI", "localPart", "prefix" |
| duration | string |
| dateTime | string with "format":"date-time" |
| date | string with "format":"date" |
| time | string with "format":"time" |
Conversion Limitations
- Restrictions/facets are not taken into consideration when
converting (
fractionDigits, pattern, totalDigits, whiteSpace,minInclusive,maxInclusive, and the restrictions for length, exceptenumeration). However, extensions and indicators are properly converted (minOccurs, maxOccurs, group, sequence, choice). - The
<documentation>element is not converted into<description>. - The
@substitutionGroupattribute for an element that has no declared type becomes a reference to the element that can substitute it. - The
@blockattribute is not taken into consideration during the conversion.
